Pipeline Overview
Pipeline Philosophy
Our pipeline implementation follows core principles of Continuous Delivery (CD) to ensure reliable, repeatable, and efficient software delivery. The pipeline serves as the foundation for:
- Automated testing at multiple levels
- Consistent deployment across environments
- Early detection of integration issues
- Rapid feedback loops for developers
- Quality gates to ensure production readiness
Pipeline Stages
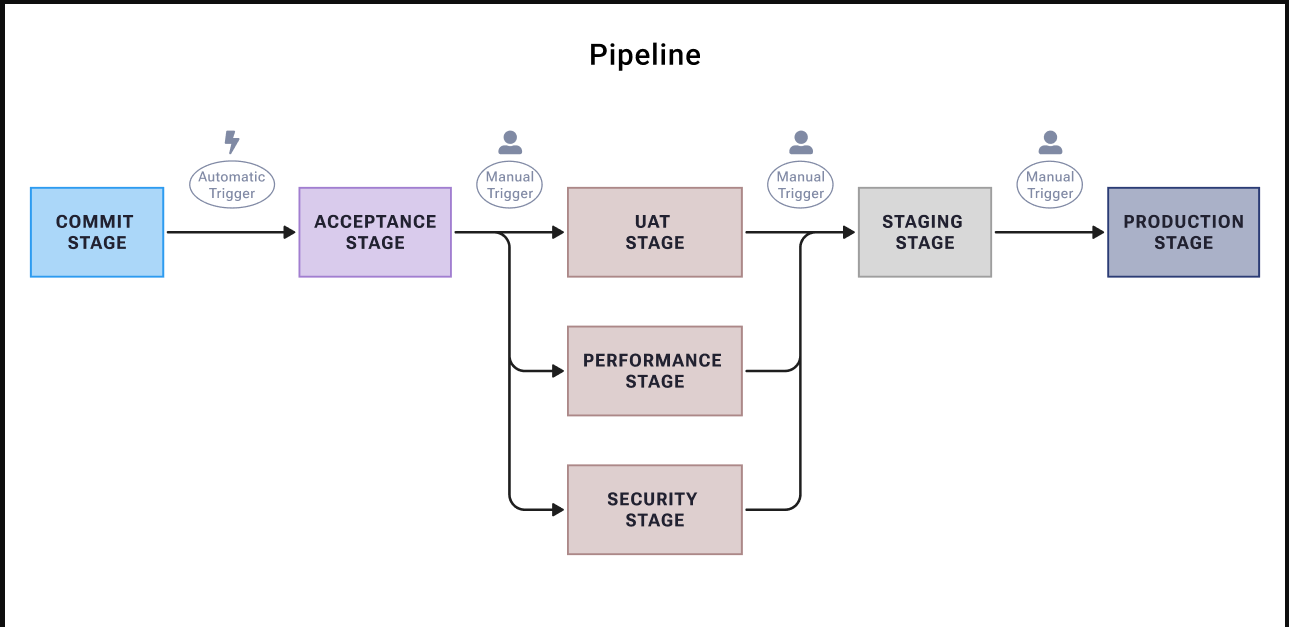
Our pipeline consists of several stages with specific triggers:
- Commit Stage: Automatically triggered on code commits
- Acceptance Stage: Automatically triggered after successful commit stage
- Parallel Stages:
- UAT Stage (Manual trigger)
- Performance Stage (Manual trigger)
- Security Stage (Manual trigger)
- Staging Stage: Manual trigger after parallel stages complete
- Production Stage: Manual trigger with approval
Stage Descriptions
Commit Stage
The first automated stage triggered by code commits. It includes:
- Component Level Tests (Unit Tests, Integration Tests)
- Code Quality Checks
- Security Scans
- Docker Image Building and Publishing
Acceptance Stage
Validates system behavior through:
- Automated Deployment to Acceptance Environment
- Smoke Tests
- Acceptance Tests
UAT Stage
Environment for manual testing:
- Automated Deployment to UAT Environment
- Smoke Tests
- Manual QA Testing
- User Acceptance Testing
Performance Stage
Validates non-functional requirements:
- Load Testing
- Stress Testing
- Scalability Testing
- Resource Utilization Analysis
Security Stage
Ensures system security:
- Security Scanning
- Penetration Testing
- Vulnerability Assessment
- Compliance Checks
Staging Stage
Production-like environment for final validation:
- Production-like Configuration
- Final Integration Testing
- Pre-production Verification
Production Stage
Final deployment stage:
- Blue-Green Deployment
- Canary Releases
- Production Monitoring
- Post-deployment Verification
Quality Gates
Each stage implements specific quality gates that must be passed before proceeding:
-
Commit Stage Gates
- All tests passing
- Code coverage thresholds met
- No critical security vulnerabilities
- Code quality metrics within acceptable ranges
-
Acceptance Stage Gates
- All acceptance tests passing
- API contract tests successful
- System integration verified
-
Environment-specific Gates
- Smoke tests passing
- Environment health checks
- Required approvals obtained
Pipeline Metrics
We track the following key metrics to measure pipeline effectiveness:
- Lead Time: Time from commit to production deployment
- Cycle Time: Time from work start to completion
- Deployment Frequency: How often we deploy to production
- Change Failure Rate: Percentage of deployments causing failures
- MTTR: Mean time to recovery from failures
Implementation Tools
Our pipeline leverages modern tooling for efficient delivery:
- Version Control: Git
- CI/CD Platform: GitHub Actions
- Container Registry: GitHub Container Registry
- Testing Frameworks: Jest, Cucumber, Playwright, Pact